SERVICES
Well- Point Dewatering
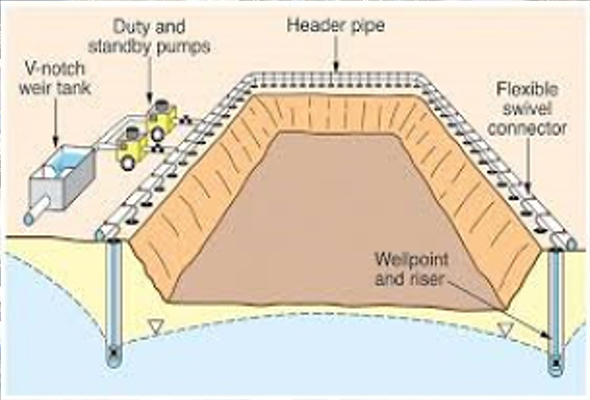
Wellpoint dewatering is one of the most effective dewatering techniques. The groundwater table is influenced by means of drawing it down through the well points that are installed around the excavation area.
Wellpoint dewatering can be used to lower and control groundwater levels in excavations, to create stable working condition.
Some of the suitable applications are pipeline construction, shallow foundations and trench works.
A typical wellpoint dewatering system will consist of calculated wellpoints which are installed at an effective standard depth and appropriate spacing around or parallel with the excavation. These wellpoints are installed into the ground using a high-pressure jetting technique, by hand or machine tooling.
The wellpoints are connected to the surface, via a riser pipe, and in turn, connected to a common header main pipe through a flexible hose.
The main header pipe is connected to a wellpoint dewatering pump and then discharged to a designated point.
PIONEERS’s Wellpoint Dewatering Systems are versatile and can be used for a wide range of applications. Our wellpoint dewatering systems will typically run 24/7 to ensure a safe working area.
Deep Well Dewatering System

Deep well dewatering system is also one of the most effective dewatering techniques and used to lower groundwater levels to provide suitable working conditions in excavations.
A deep well typically consists of a borehole fitted with a slotted casing and an electric submersible pump. As water is pumped from a deep well, a hydraulic gradient is formed and water flows into the well forming a cone of depression around the well in which there is little or no water remaining in the pore spaces of the surrounding soil.
A deep well is installed using an outer and inner casing. The void between the outer and inner casing is packed with gravel to act as a filter medium. The inner casing is slotted to allow for ingress of water. Submersible pumps are lowered into the inner casing to allow for high head pumping. The pumps are engineered to withstand the aggressive corrosion factors associated with use over sustained periods of time in a saline environment.
Deep Well dewatering technique is particularly suited to deeper excavations.
The system is reliable and the wide spacing of the wells reduces access restrictions to a minimum.
Deep wells can be installed in a ring around or within the excavation to lower the water level and maintain suitable working condition.
Our experienced team analyses information, and design deep well dewatering system and works with the operations team to strategically position wells around and within
the excavation area. The PIONEERS’s deep well system economically and reliably lowers the water table with little disruption to the excavation and construction process.
Deep wells are also used for aquifer testing and for groundwater drainage by wells.
Slump Pumping & Trenching Dewatering System
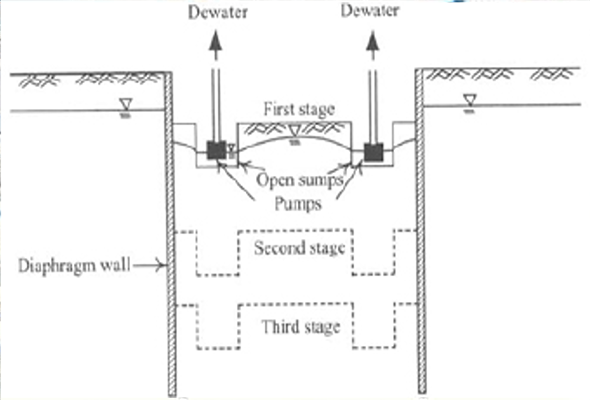
This is the most economical method of dewatering as gravity is the main playing force.
Sump is created in the excavated area into which the surrounding water converges and accumulates facilitating easy discharge of water through pumping system.
Its application is however confined to the areas where soil strata is hard. Since the bottom of the sump is situated at a level lower than that of the excavation bottom, it will abridge the seepage way along which groundwater from outside seeps into the excavation zone and as a result the exit gradient of the sump bottom will be larger than that on the excavation surface.
If the excavation area is large, several sumps may be placed along the longer side or simply use a long narrow sump which is called a trench.
Hydrogeological Groundwater Modelling
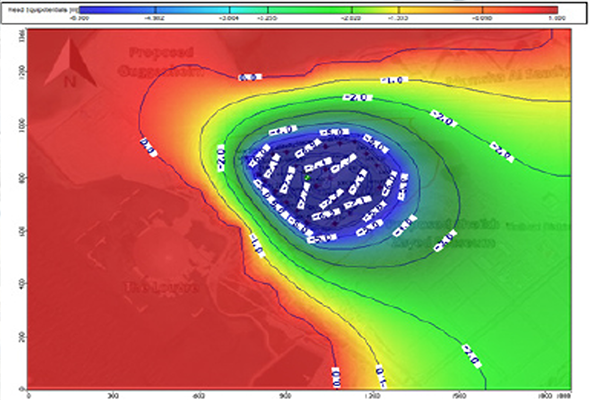
Groundwater models are used to predict the effects of hydrological changes (like groundwater abstraction or irrigation developments) on the behaviour of the aquifer and are often named groundwater simulation models.

The model is considering features as:
• The geometry and properties of known aquifer systems.
• The geology of the site and the impact of the proposed structure(s) on groundwater flow.
• The layout of the construction areas and the proposed site.
The model can be used to refine, predict, and quantify the required dewatering system for construction and the potential environmental impacts associated with dewatering.
The aim of the groundwater flow modelling is to assess dewatering requirements and associated groundwater drawdown impacts of the proposed project. The model is based on current conceptual hydro geological understanding.
Diesel Dewatering Pumps


Diesel Operated Tower Lights

